Quick Navigation :
What Is exFAT?
exFAT is an acronym for Extended File Allocation Table which is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006. It is created to be used on flash memory like USB flash drives, SD cards and so on.
The biggest difference between exFAT vs NTFS is Mac os support. ExFAT offers full read-write support for mac while NTFS offers only read only support for mac. ExFAT is also compatible with some devices that don't support NTFS like digital camera. FAT32 means File allocation Table. Lack of exFAT / NTFS support is another big drawback of CDJs. Telling customers to use 3rd party tool for formatting to FAT32 is NOT a solution. If a $600 Numark NDX-900 can afford to get NTFS license from Microsoft, then it should be possible for Pioneers much more expensive products like $2000 CDJ-2000nxs(2). However, FAT32 and exFAT work with all operating systems by default. FAT (File Allocation Table) is the oldest of these file systems, and is hence recognized by every operating system. For personal computers, the first one used was FAT12, followed by FAT16, and then the current FAT32. ExFAT fixes the downsides of the FAT32 file system regarding maximum file size and partition size. Another advantage is that it keeps the high compatibility with many operating systems and devices. Another upside is the increase in speed when transferring data when compared with FAT32. The name of exFAT gives a hint for its precursors: FAT file system. ExFAT is a newer version of the FAT32 file system, and you can think it this way: it is a middle ground between FAT32 and NTFS file system (New Technology File System). The Pros of exFAT. ExFAT is a file system that is optimized for flash drives.
The name of exFAT gives a hint for its precursors: FAT file system. exFAT is a newer version of the FAT32 file system, and you can think it this way: it is a middle ground between FAT32 and NTFS file system (New Technology File System). Building symbol text.
The Pros of exFAT
exFAT is a file system that is optimized for flash drives. For that purpose, exFAT has some of the main features that distinguish it from other file systems:
- exFAT is a lightweight file system that does not require maintenance of a large amount of hardware resources.
- It offers support for huge partitions, of up to 128 pebibytes, while 512 exbibytes is recommended.
- It supports huge file stored that is much larger than the 4GB limit imposed by FAT32. If you're curious, the theoretical file size limit is 16 exbibytes, but this exceeds the maximum partition dimension, so the actual size limit of a file stored on exFAT is the same as the partition limit: 128 pebibytes.
- Cluster size up to 32MB.
- exFAT adopts the remaining space allocation table, the performance of remaining space allocation improved.
- The maximum number of files in the same directory can reach 2,796,202.
- exFAT is more compatible with a lot of devices and operating systems than NTFS.
The Cons of exFAT
exFAT lacks the support of journaling (in fact, to some extent it is not a disadvantage, and we will explain the reasons in the next part). The journaling feature allows the file system to keep records of the changes made to the files stored on it. This is useful when data corruption occurs because the logs can be used to recover corrupted data.
exFAT does not have this feature, which means that data can be more susceptible to corruption in the event of an unexpected shutdown or the inability to safely eject a removable drive formatted in this way.
Its file allocation tables and file allocations themselves do not support multi-user environments and are susceptible to large file fragmentation. Few other file systems have this issue.
It is not quite as widely-supported as FAT32 does.
What's the Benefits When You Choose exFAT for A Removable Media
Exfat Or Fat32 Usb
We take the USB flash drive as an example to explain this issue. First of all, we mentioned that exFAT is between FAT and NTFS. Though for performance it cannot compare to NTFS, it does have features better than FAT32 which you can find in the pros of exFAT(last part).
Here we list one typical point. The USB flash drive which is formatted with FAT32 file system cannot have a single file over 4GB. Although there are few opportunities for a single file to exceed 4GB, it does not mean that there are not: original files for BD/HD movies, uncompressed audio files for lossless music lovers, ISO files for DVDs, etc., if you want a full backup, you must choose exFAT over FAT32 as the storage format.
Then you might ask why not choose NTFS? Yes, NTFS is a more powerful file system, but it is targeted 'log' file system requires frequent recording of disks during reading and writing, while a USB flash drive has a limit on the number of reading and writing, therefore, theoretically a USB flash drive which uses the NTFS format will have a relatively short lifetime. And the compatibility is a problem too.
What's more? The exFAT file system is compatibility with both Windows and Mac, so if you want to transfer data between computers with these two different operating systems, formatting a USB flash drive with exFAT is the best choice.
Exfat Or Fat32 For Linux

The name of exFAT gives a hint for its precursors: FAT file system. exFAT is a newer version of the FAT32 file system, and you can think it this way: it is a middle ground between FAT32 and NTFS file system (New Technology File System). Building symbol text.
The Pros of exFAT
exFAT is a file system that is optimized for flash drives. For that purpose, exFAT has some of the main features that distinguish it from other file systems:
- exFAT is a lightweight file system that does not require maintenance of a large amount of hardware resources.
- It offers support for huge partitions, of up to 128 pebibytes, while 512 exbibytes is recommended.
- It supports huge file stored that is much larger than the 4GB limit imposed by FAT32. If you're curious, the theoretical file size limit is 16 exbibytes, but this exceeds the maximum partition dimension, so the actual size limit of a file stored on exFAT is the same as the partition limit: 128 pebibytes.
- Cluster size up to 32MB.
- exFAT adopts the remaining space allocation table, the performance of remaining space allocation improved.
- The maximum number of files in the same directory can reach 2,796,202.
- exFAT is more compatible with a lot of devices and operating systems than NTFS.
The Cons of exFAT
exFAT lacks the support of journaling (in fact, to some extent it is not a disadvantage, and we will explain the reasons in the next part). The journaling feature allows the file system to keep records of the changes made to the files stored on it. This is useful when data corruption occurs because the logs can be used to recover corrupted data.
exFAT does not have this feature, which means that data can be more susceptible to corruption in the event of an unexpected shutdown or the inability to safely eject a removable drive formatted in this way.
Its file allocation tables and file allocations themselves do not support multi-user environments and are susceptible to large file fragmentation. Few other file systems have this issue.
It is not quite as widely-supported as FAT32 does.
What's the Benefits When You Choose exFAT for A Removable Media
Exfat Or Fat32 Usb
We take the USB flash drive as an example to explain this issue. First of all, we mentioned that exFAT is between FAT and NTFS. Though for performance it cannot compare to NTFS, it does have features better than FAT32 which you can find in the pros of exFAT(last part).
Here we list one typical point. The USB flash drive which is formatted with FAT32 file system cannot have a single file over 4GB. Although there are few opportunities for a single file to exceed 4GB, it does not mean that there are not: original files for BD/HD movies, uncompressed audio files for lossless music lovers, ISO files for DVDs, etc., if you want a full backup, you must choose exFAT over FAT32 as the storage format.
Then you might ask why not choose NTFS? Yes, NTFS is a more powerful file system, but it is targeted 'log' file system requires frequent recording of disks during reading and writing, while a USB flash drive has a limit on the number of reading and writing, therefore, theoretically a USB flash drive which uses the NTFS format will have a relatively short lifetime. And the compatibility is a problem too.
What's more? The exFAT file system is compatibility with both Windows and Mac, so if you want to transfer data between computers with these two different operating systems, formatting a USB flash drive with exFAT is the best choice.
Exfat Or Fat32 For Linux
In summary, if you want to format a USB flash drive but don't know which file system to choose, here are the advices:
- It is generally recommended to use the FAT32 format, which has the greatest compatibility.
- If you want a better performance experience, want to store large files, or use the drive between Mac and Windows, you can choose the exFAT format (might not be recognized by some devices other than the computer).
- NTFS format is not recommended.
In a Windows-based environment, USB flash disks may be formatted using three different file systems: FAT32, exFAT and NTFS. The FAT32 file systemis a mature file system, which is an improved version of the original FAT file system used in the MS DOS operating system. Later, Microsoftintroduced the NTFS file system, which improved the performance and reliability of file operations. Finally, in 2006 Microsoft added the exFATfile system, which is especially optimized for flash devices and resource constrained hardware configurations.
- FAT32 - a mature file system normally used on USB disks
- exFAT - a newer file system optimized for flash devices
- NTFS - an advanced, journaling file system
Normally, USB flash disks are sold formatted using the FAT32 file system. But, is it an optimal file system to be used with modern USB3 flash disks?Which of the available file systems is more optimized for small files and which one is more optimized for large files? Which of the available filesystems is more optimized for read operations and which one is more optimized for write operations? In order to answer these questions, we havetested three different USB3 flash disks using a diversified set of benchmarks.
- USB3 Disk 1 - Silicon Power Blaze B20 16GB
- USB3 Disk 2 - Transcend JetFlash 780 16GB
- USB3 Disk 3 - SanDisk Extreme 16GB
An identical set of tests has been performed on each USB3 flash disk three times and before each test USB3 disks were reformatted using the FAT32,exFAT and NTFS file systems respectively. All tests were performed using DiskBoss v4.7.28, which is capableof analyzing disk space usage, classifying files, searching duplicate files, synchronizing files, copying files and deleting files using a numberof parallel threads. Each USB3 disk for each file system has been tested using an identical set of benchmarks including: Web search software download.
- Test 1 - Small Files Write To USB Disk Test (18,000 Files, 1 GB of Data)
- Test 2 - Small Files Read From USB Test (18,000 Files, 1 GB of Data)
- Test 3 - Medium Files Write To USB Disk Test (100 Files, 1GB of Data)
- Test 4 - Medium Files Read From USB Disk Test (100 Files, 1 GB of Data)
- Test 5 - Large Files Write To USB Disk Test (10 Files, 1 GB of Data)
- Test 6 - Large Files Read From USB Disk Test (10 Files, 1 GB of Data)
- Test 7 - Disk Space Analysis Test (20,000 Files, 4 GB of Data)
- Test 8 - Duplicate Files Search Test (20,000 Files, 4 GB of Data)
- Test 9 - File Delete Operations Test (20,000 Files, 4 GB of Data)
Benchmark results from all USB3 flash disks using three different file systems were normalized and compared relative to the performanceof the FAT32 file system, which is by default used on all USB3 flash disks. Adobe cs6 design standard arabic enabled amtib for mac osx.
According to the average benchmark results, which shows a normalized average performance for all types of benchmarks for each file systemrelative to the FAT32 file system performance, the NTFS file system delivers up to 19% of performance improvements and the exFAT filesystem delivers up to 7% of performance improvements over the normally used FAT32 file system.
https://herepfil761.weebly.com/rocket-typist-1-3-expand-typed-abbreviations-copy.html. For users required to write a large number of small files to a USB3 flash disk, the NTFS file system can deliver up to 40% of performanceimprovements and the exFAT file system up to 25% of performance improvements over the normally used FAT32 file system.
For users required to read a large number of small files from a USB3 flash disk, the NTFS file system can deliver up to 10% of performanceimprovements and the exFAT file system up to 2% of performance improvements over the normally used FAT32 file system.
For users required to write medium-sized files to a USB3 flash disk, the situation changes and the exFAT file system takes the lead withup to 4% of performance improvements over the normally used FAT32 file system while the NTFS file system drops 1% below.
When reading medium-sized files from a USB3 flash disk, the exFAT file system delivers up to 9% of performance improvements and the NTFSfile system delivers up to 5% of performance improvements over the FAT32 file system. Excel 2007 vs 2010 differences.
When writing a small number of large files to a USB3 disk, the mature FAT32 file system outperforms the exFAT file system by 2% and the NTFSfile system by 11% making it clear that the NTFS and exFAT file systems are more optimized for large numbers of small files while the simplerFAT32 file system takes the lead when working with a small number of large files.
When reading a small number of large files from a USB3 disk, all three file system performed almost identically with a small 2% performanceimprovement for the exFAT file system and an even smaller 1% performance improvement for the NTFS file system.
For disk space analysis and file classification operations, which mostly require to read directory structures from the USB3 disk, the simplerFAT32 file system takes the lead with up to 10% performance improvements over the exFAT and NTFS file systems.
For duplicate files search operations, which require a large number of random read operations, the NTFS file system delivers up to 40% ofperformance improvements over the normally used FAT32 file system, while the exFAT file system drops 2% below.
Audiobook builder 2 0 1 download free. For file delete operations, the NTFS file system delivers up to 68% of performance improvements and the exFAT file system delivers upto 24% of performance improvements over the normally used FAT32 file system.
In addition to the explained performance tests, we have monitored the test computer using the SysGauge system monitoring utility,which is capable of monitoring the disk transfer rate, file system performance and operating system resource usage and generate various types of graphical performance monitoring reportsshowing what exactly happened inside of the computer during the performed performance tests.
For each tested file system, we have copied exactly the same set of files and during each file copy operation monitored the following operating system performance counters:
- File System Control IOPS - this counter shows how much I/O operations where nether read or write operations, which means that these operations are actually the file system overhead required for the file system itself to operate properly and a file system with less overhead is obviously better.
- Total Number of System Calls - this counter shows now many system calls were performed by the operating system in order to complete the file copy operation. Each system call requires CPU and system resources and therefore a file system capable of completing the file copy operation using less system resources is better.
- Total Number of CPU Context Switches - this counter shows now many CPU context switches were performed by the operating system in order to complete the file copy operation. Each context switch requires CPU and system resources and therefore a file system capable of completing the file copy operation using less system resources is better.
For example, as it is shown on the following SysGauge performance monitoring report, in order to complete the file copy operation,the NTFS file system performed 86,243 file system control operations, the exFAT file system performed 87,101 file system control operations and the FAT32 file system performed 109,577 filesystem control operations. Clearly, the FAT32 file system has a significantly higher file system overhead compared to the NTFS and exFAT file systems.
According to the system calls monitoring chart, during the file copy operation, the operating system performed 809,100 system calls when copying data to the NTFS file system,967,800 system calls in order to copy the same set of files to the exFAT file system and 1,144,200 system calls when copying the same set of files to the FAT32 file system.Once again, the NTFS file system manages to complete the file copy operation using less system resources, the exFAT file system comes in the second place and the FAT32trailing the list with the most system overhead.
Finally, according to the CPU context switches chart, when copying the set of files to the NTFS file system, the operating system performed 908,300 context switches.On the other hand, the exFAT file system required 1,362,300 CPU context switches to copy the same set of files and the FAT32 file system required 1,547,900 contextswitched to perform the same file copy operation.
The NTFS file system consistently shows better efficiency and lower CPU and system resource usage when compared to the exFAT file system and the FAT32 file system,which means file copy operations are completed faster and more CPU and system resources are remaining for user applications and other operating system tasks.
- FAT32 File System - if the user needs to work with a relatively small number of medium-sized or large files, the FAT32 file system is good enough to be used with modern USB3 flash disks.
- exFAT File System - if the user needs to work with thousands of files stored on a USB3 disk and perform different types of operations, it is recommended to reformat the USB flash disk using the exFAT file system.
- NTFS File System - if the user needs to work with tens of thousands of files stored on a USB3 flash disk and perform many different types of operations, it is highly recommended to reformat the USB flash disk using the NTFS file system.
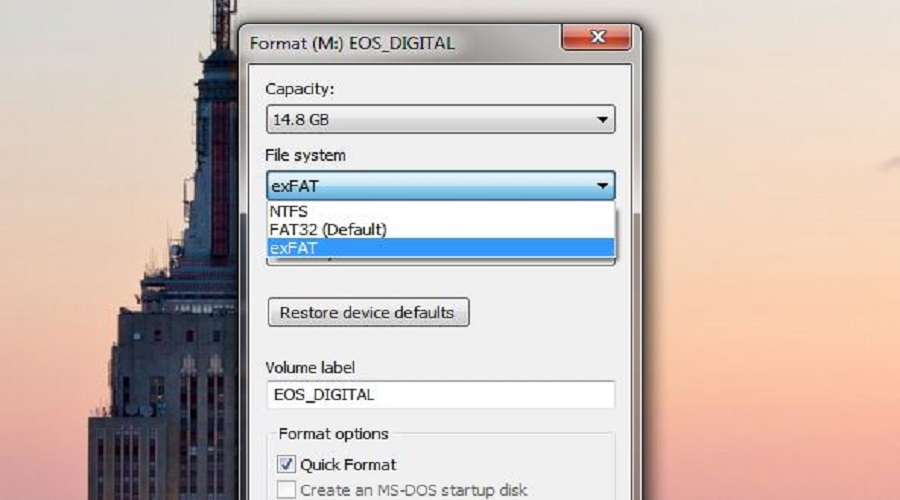
In order to reformat a USB flash disk in Windows 7, open the Windows Explorer application, select the 'Computer' item in the left-side view,select the required USB flash disk in the right side view, click the right mouse button and select the 'Format' menu item.
On the 'Format Disk' dialog, select an appropriate file system to format the USB flash disk with, enter a disk label, and press the 'Start' button.
WARNING: The disk format operation will permanently erase all files stored on the USB flash disk. Before performing a disk format operation,backup all files from the USB flash disk to a different disk in your computer or an external storage device.
* This performance review has been prepared for information purposes only and we strongly advise you to make your own performance evaluations using your specific hardware components and datasets.

